Science Projects
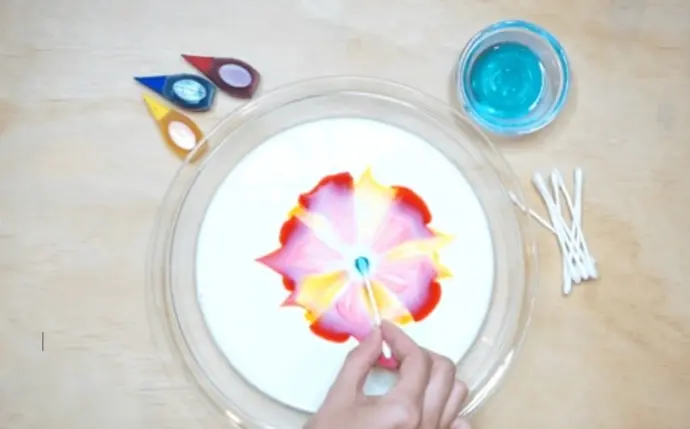

Dancing Colors
The objective of the Dancing Colors science project is to demonstrate how different substances interact, particularly how dish soap affects the fat molecules in milk. This interaction causes the food coloring to move and create a colorful "dance" on the surface of the milk.
This experiment helps students grasp the idea of how different substances (like soap, milk, and food coloring) can interact and cause visible changes.
Project Introduction: Dancing Colors
The Dancing Colors science experiment is a fun and colorful way to explore the fascinating world of chemistry and physics!
Milk is made up of water, fats, and proteins. When dish soap is added to the milk, it breaks down the fat molecules and changes the surface tension of the milk. This causes the food coloring, which initially sits still on the surface of the milk, to move and swirl in different directions.
Through this experiment, we will learn about important scientific concepts like surface tension, chemical reactions, and how substances interact in surprising ways. It's not just a fun visual activity, but also a chance to understand how everyday items, like dish soap and milk, can work together to create something amazing!
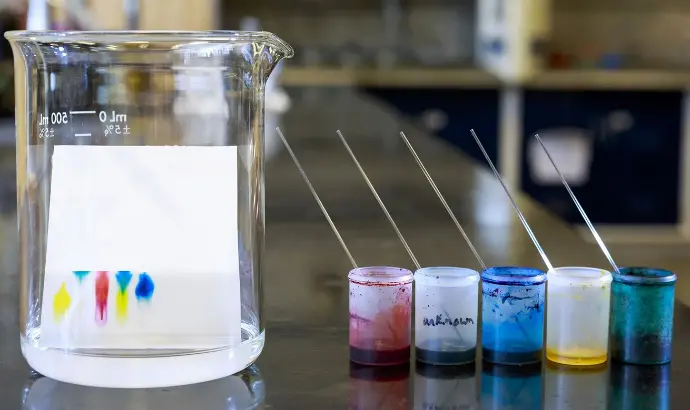

Chromatography
Objective - The chromatography project's objective is to separate a mixture's components based on their different properties.
Explanation
Chromatography is a technique used to separate mixtures based on their different properties. In this experiment, the different components of the ink or food coloring have different affinities for the filter paper and the water. As the water moves up the paper, it carries the different components at different rates, causing them to separate.
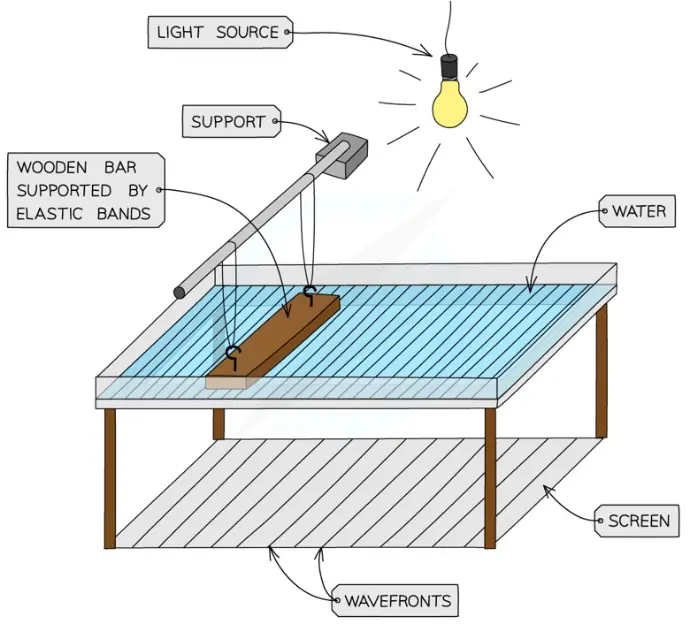
Wavey Wonder
Objective - To understand the concept of wave propagation.
To learn about the properties of waves, such as wavelength, frequency, and amplitude.
To observe how waves interact with different types of obstacles.
Explanation - A wave is a disturbance that travels through a medium, transferring energy from one point to another without the physical transfer of matter. When you create a wave in water, you're disturbing the water's surface, causing ripples to spread outward.
When a wave encounters an obstacle, its behavior depends on the size of the obstacle relative to the wavelength: diffraction, refraction, reflection
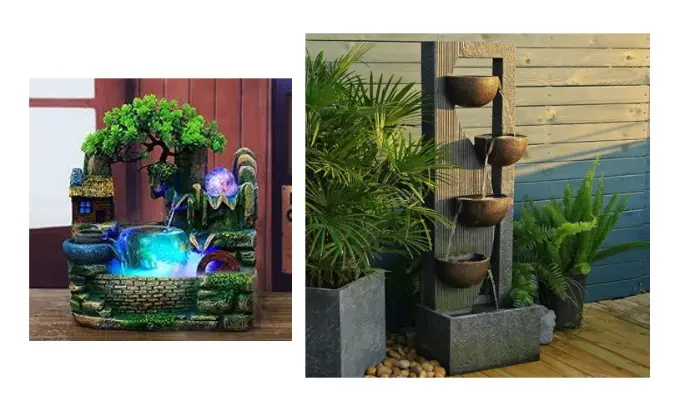

Water fountain without electricity
Objective of the Project:
To show the model of a water fountain without electricity by understanding the phenomenon of hydraulic pressure. At the same time, students will have awareness about using clean energy resources.
Project Introduction:
The fountain without electricity operates based on the principle of hydraulic pressure and gravity. The water flows from a higher level to a lower level, creating pressure that drives the water upward through a spout without the need for an external power source, often using devices like siphons or hydraulic pumps.

Decomposer
Objective of the project:
Students will be able to recognize how the decomposers are taking nutrients from the other resources.
Project introduction:
Among 4 decomposers, students are growing mushrooms as one type of decomposer. They are also investigating how sunlight and water affect the growth of mushrooms. Different amounts of sunlight and water will decide the different growth of mushrooms.

Grow Like a Pro
The Science of Better Planting for sustainable agriculture
Objective:
To explore and identify the ideal soil composition, water levels, and sunlight conditions for optimal plant growth, enabling students to apply scientific methods for successful gardening and contribute to sustainable environmental practices.
Project Introduction:
This agricultural Project examines the relationship between soil composition, water quantity, and plant growth by testing varied soil types (mixed, red, and planting soil) and water levels to identify optimal growth conditions. It uses controlled variables (soil type and water amount) to observe differences in plant health, demonstrating how soil properties and hydration influence nutrient availability, root development, and photosynthesis rates for improved growth outcomes.

Light spectrum: Illuminating plant growth
Objective: The objective of this project is to investigate the impact of different light wavelengths on plant growth. By exploring the light spectrum, the project aims to determine which colors or types of light most effectively promote plant health and development.
Project Introduction: This project focuses on the role of light in plant growth, particularly how varying wavelengths from the light spectrum—such as red, blue, and yellow light—affect photosynthesis and overall plant health. By using different light sources, the project seeks to uncover how specific colors of light can enhance or hinder the growth of plants, offering insights into optimizing growing conditions for plants, especially in controlled environments like indoor gardens or greenhouses. plants grow tallest and healthiest under blue and red light due to effective chlorophyll absorption, while yellow light has the least positive impact on growth.

Static Wonders
Objective: The objective of this project is to demonstrate the principles of static electricity and electrical charge through the construction and operation of a Van de Graaff generator. The project aims to explore how a high-voltage electrostatic generator can accumulate and discharge electrical energy, and its applications in scientific experiments and technology.
Project Introduction: The Van de Graaff generator is a device that produces high voltages through the accumulation of electrical charge on a metal sphere. This project will involve building and operating a Van de Graaff generator to observe phenomena such as electric sparks, the behavior of charged objects, and the effects of static electricity on various materials. By experimenting with this generator, the project aims to better understand the principles of electrostatics, electrical potential, and charge transfer, which have various applications in fields like particle physics, medical treatments, and even everyday electrical devices.

Thermal generator
Objective of the Project:
Learn how to produce heat for industrial purpose, provide district heating, or desalinate water, in addition to generate electrical power.
Project Introduction:
The principle behind a thermal generator is the conversion of thermal energy into electrical energy through thermoelectric materials, utilizing temperature differences to produce heat for industrial applications, district heating, desalination, and power generation.
Using a thermal
generator at home can lead to significant cost
savings by lowering electricity bills, especially when utilizing
waste heat from renewable energy sources. This technology not only improves home efficiency by
harnessing otherwise wasted thermal energy, but it also contributes to a reduced carbon footprint by
minimizing reliance on non-renewable energy sources.
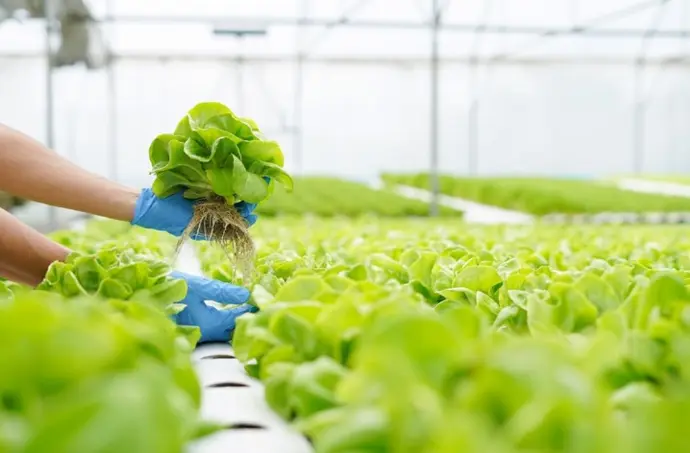

Hydroponic Plantation
The objective of a hydroponic plantation project is to explore and demonstrate the feasibility of growing plants without soil, using a nutrient-rich water solution to deliver essential nutrients directly to the plant roots. The project aims to understand the principles of hydroponics and study the science and techniques behind soil-free plant cultivation.
Ultimately, the project encourages the adoption of innovative farming methods that could lead to more sustainable and efficient agricultural practices.
Project Introduction:
Hydroponic PlantationHydroponic plantation is an innovative and sustainable method of growing plants without the use of soil. Instead, plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution, which allows the roots to absorb essential minerals and nutrients directly. This method offers numerous advantages over traditional soil-based farming, including water conservation, faster plant growth, and the ability to grow crops in areas with poor or contaminated soil.
By creating a small-scale hydroponic system, we will experiment with different plants, monitor their growth, and assess the effectiveness of various hydroponic techniques.
With the increasing global population and the growing challenges of climate change and limited arable land, hydroponic farming offers a promising solution to meet the food demands of the future. Through this project, we aim to gain a deeper understanding of how hydroponic systems work and how they can be applied to enhance agricultural practices.

Biodegradable plastics
Objective of the Project:
To raise awareness about the significance of plastic pollution and how it impacts our planet negatively.
To gather components for environmentally friendly plastic samples in order to identify strategies for reducing the danger of contaminating the planet.
Project Introduction:
Biodegradable plastics are designed to break down naturally in the environment, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional plastics that can persist for hundreds of years. Made from renewable sources like cornstarch, sugarcane, or potato starch, these plastics decompose through microbial activity, turning into natural compounds that are less harmful to ecosystems. The development and use of biodegradable plastics aim to reduce plastic pollution, lower the impact on landfills, and promote a circular economy focused on environmental health.
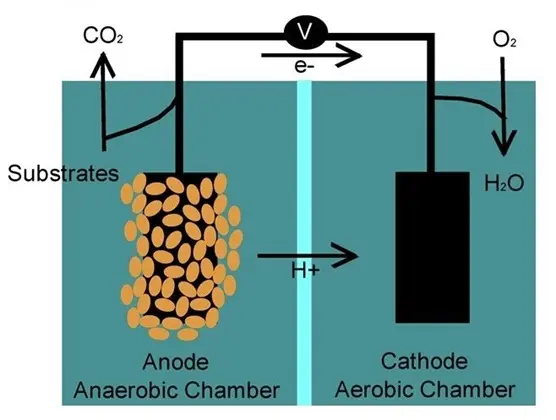
Microbial fuel cell
Objective of the Project:
Learn what a microbial fuel cell is, how it works and why it’s useful. Expanding the knowledge of students on the different ways energy can be harnessed sustainable ways even if they are unusual ones.
Project Introduction:
The microorganisms in the anode electrode oxidize the organic matter, breaking down pollutants and generating electrons that flow through an electrical circuit to the cathode compartment. This process also generates clean water as a byproduct, which can be reused or released back into the environment.

Musical Acoustics
Learning Goal_ To understand the scientific principles of sound production and transmission in musical instruments
Scientific Principles:
- Sound Waves: Sound is produced when an object vibrates, creating pressure waves in the air. These waves travel through mediums (air, water, or solid) and are perceived as sound by our ears.
- Frequency and Pitch: The frequency of a sound wave determines its pitch. High-frequency waves produce high-pitched sounds, while low-frequency waves produce low-pitched sounds.
- Amplitude and Volume: Amplitude refers to the height of sound waves. Larger amplitudes result in louder sounds, while smaller amplitudes are perceived as quieter.
- Resonance: When the frequency of a sound matches the natural frequency of an object, it causes the object to vibrate more strongly. This principle is used in musical instruments to amplify sound.
- Timbre: This is the quality or color of sound that makes different instruments or voices sound unique, even when they produce the same note.
Real-Life Applications:
- Instrument Design: Understanding sound waves helps in designing instruments that produce desired tones.
- Concert Hall Acoustics: Engineers use the principles of acoustics to design concert halls that enhance sound quality, ensuring that every listener experiences clear and balanced sound.
- Hearing Aids: The study of sound waves and frequencies aids in the development of devices that amplify sound for individuals with hearing loss.
- Music Production: Sound engineers use acoustic principles to mix and balance sound in recordings, ensuring clarity and richness in music.
#24/12 , Kan Baw Za St, ( Wun Gyi St. ) , Yae Aye Quin Qtr, Taunggyi, Myanmar.
✉ tgy@brainworksschool.com
☎
(95)9 891432514 , (95)9 883344738